Types of medical and pedagogical control in athletics. Athletics. Biochemical study allows you to determine the concentration of the most important chemical compounds and the activity of enzymes
Chapter 3. Medical and pedagogical control over physical training
Features of the methodology training sessions in various sections physical training
FP classes are organized and conducted in the following sections: applied gymnastics, athletics, accelerated movement (march), overcoming obstacles, fighting techniques, ski training and swimming and swimming.
The main content of the section "Applied gymnastics": pulling up and lifting with a coup on the crossbar, raising the legs to the crossbar, bending and unbending the arms in emphasis on the uneven bars, etc. A feature is the organization strength training on projectiles, simulators and the use in each lesson of exercises for surprise, speed of action, requiring the manifestation of speed-strength abilities.
Athletics. Content: running for short (100.200.400 m), medium (800.1000.1500 m) and long (3000.5000.10000 m) distances.
Teaching the technique of performing these exercises is carried out mainly by the method of “learning as a whole”. Before practicing running techniques for short, medium and long distances, grenade throwing, shot put and jumping, an additional warm-up is carried out.
Fast travel(march) for 6, 10 km. Feature: carried out on rough terrain (if possible in uniform with weapons and equipment). When preparing for a forced march, it is necessary to increase the load from one lesson to another by gradually increasing the distance and its segments covered by running, by complicating the route of movements, etc.;
Overcoming obstacles. Feature: classes are held on specially equipped obstacle courses and on terrain with natural obstacles and barriers. Learning to overcome obstacles is carried out at the beginning without a weapon, then with a weapon, and training - with a gradual increase in the weight of the calculation, the complication of the conditions for overcoming obstacles.
Fighting techniques fight. Classes are held both in a hall with a special coating, equipped with boxing and wrestling equipment, and in a specially prepared pit with sand and sawdust, on the ground, as well as in conditions that simulate a certain operational situation. To avoid injury while exercising Special attention is given to the preparation of places of employment, the body of students to perform techniques, the discipline of those involved. Painful techniques during training are performed smoothly, without jerks, and at the signal of the partner (claps on the body or voice - “Yes”) immediately stop. Throws are carried out from the middle to the edges of the carpet. Learning the techniques of self-insurance and insurance is carried out in the first lessons, and in the future they are constantly being improved. Training in techniques is carried out in pairs, approximately equal in height and weight. Techniques and actions related to the performance of strikes, throws and painful techniques are studied and improved in both directions, with the right and left limbs, first at a slow and then at a fast pace. When teaching disarmament techniques in the classroom, models of knives, pistols, machine guns and other items are used.
Ski training. Features: at the first lesson, the leader checks the ability of the personnel to ski. For non-skiers, the first 2-3 lessons are held separately. For learning skiing a flat area protected from the wind (approximately 50 x 80 m in size) is selected, on which two closed ski tracks are laid 5-10 m from one another. The movement on the ski tracks is carried out in one direction.
Swimming and swimming. Classes are held at specially equipped reservoirs, water stations, in indoor and outdoor pools at a water temperature of at least +17°C. In the first swimming lessons, as well as during the ski training the ability to swim is checked and the personnel are divided into three groups:
· the first group - not able to swim, not swimming 25 m;
· the second group - able to swim, swimming 25 m, but not owning one of the most beneficial ways of swimming in terms of service and application (on the side, breaststroke);
The third group - the most trained swimmers who own one of the indicated methods and swim at least 200 m.
Physical exercises affecting the human body, bring it out of the state of homeostasis (constancy and stability of the internal environment). Due to various reactions of organs and systems, the body returns to a homeostatic state after the cessation of exercise. Therefore, for proper organization and conducting classes on PT knowledge of the physiological patterns of the body's activity during classes exercise and basic methods of assessing his reaction is absolutely necessary. This applies not only to specialists in the field of FP, but also to everyone who has anything to do with it (who is engaged in it independently, who organizes, who manages the process of FP).
Cadets, in the future officers of the Ministry of Emergency Situations, have the most direct relation to the FP process. Therefore, they must necessary minimum knowledge in the field of regulation of physical activity and determination of the body's response in the process of PT.
Medical and pedagogical control (MPC) is an important part of medical supervision of the health of people involved in physical culture or its applied form - physical training. It determines the improvement of the process of physical education and sports training in order to optimize the health-improving orientation and enhance the training impact of physical exercises.
The military-industrial complex is a set of measures that allow assessing the effectiveness of PT classes on the body of those involved and is carried out by PT specialists together with representatives medical service. Separate measures for the military-industrial complex can be carried out by commanders (chiefs) of all levels and by the students themselves.
The goal of the military-industrial complex is to improve physical condition involved, which combines physical development, functional state and physical fitness of a person.
To achieve this goal, it is necessary in the process of military-industrial complex to solve the problems medical support FP, which are specified in the following aspects:
determination of adequacy physical activity on various forms of FP level physical development, functional state and physical fitness cadets;
assessment of the dynamics of various indicators of the physical condition of students during the semester, school year;
injury prevention.
We will talk about the first two directions in the subsequent educational questions of the lecture, and now we will note the main components of injury prevention:
monitor the serviceability of sports equipment, facilities, exercise equipment, sports shoes and clothing;
observe the correct methodology and rational organization of classes;
Maintain discipline in the classroom and comply with the requirements for the implementation of physical exercises and the rules of sports competitions;
provide competent insurance and assistance in performing complex exercises;
to monitor the condition of those involved;
- carry out explanatory and propaganda work on the need and importance of preventive work to prevent injuries in PT classes.
on this topic:
METHODS OF CONTROL AND RECOVERY IN THE TRAINING PROCESS OF ATHLETES
Designed by:
Shuvalova Anastasia Nikolaevna
instructor-methodologist
2017
Introduction
Methods of pedagogical control
1.1 Types of pedagogical control
Methods of biochemical control
2.1. Blood tests
2.2. Urinalysis
2.3. Exhaled air
2.4. Saliva tests
2.5. Sweat analyzes
2.6. Biopsy of muscle tissue
Instrumental control methods
Recovery methods in athletics
4.1. Massage
4.2. Bath
Conclusion
References
Introduction
Everyone knows that in order to achieve high sports results, modern athletes of any sport need to work hard. Athletes-athletes, who in the training process have to perform loads of large volumes and high intensity, are no exception.
The volume and intensity of the load are the external sides of the magnitude of the impact of physical exercises on the body of those involved. Inner side physical load is determined by those functional changes that occur in the body of an athlete due to the influence of external parties. Thus, the loads used during physical training act as an irritant that stimulates adaptive changes in the body. In order for the training effect to be proper, it is necessary to influence the body of an athlete, taking into account his individual adaptive abilities to loads. Thus, throughout the entire training process, it is necessary to monitor the changes taking place at this time in the body of an athlete. Thus, the purpose of control is to optimize the process of an athlete's sports training based on an objective assessment of various aspects of his preparedness.
Means and methods of control can be of a pedagogical, psychological, biomedical nature. Based on this, there are several types of control: pedagogical, medical, psychological, biomechanical, biochemical, self-control, etc. The possibility of using several types of control over athletes at once depends to a greater extent on the material base sports schools and schools (the presence of a sports psychologist, a doctor, the availability of appropriate equipment, etc.). The results obtained by several types of control at once give a more complete picture of the adaptive changes in the athlete's body and allow you to make accurate changes in the training process.
The process of functional changes occurring in the body of an athlete is influenced by coaches not only by varying the load, but also by using various means of recovery. Knowledge of the patterns of recovery allows you to use a wide arsenal of tools to speed up recovery processes. Usually, psychological, pedagogical and medical-biological means of recovery are distinguished. The latter, in turn, include: hygienic (mode, full sleep and rest, condition of clothing, equipment, inventory), physical (massage, bath, hydroprocedures, electroprocedures, light exposure, hyperoxia, magnetotherapy, ultrasound, laser, phonophoresis), balanced in composition , energy, corresponding to the nature of the load, climatic and weather conditions nutrition, pharmacological (energy, plastic substances, vitamins and minerals, adaptogens, hepatoprotectors, substances that stimulate hematopoiesis, immunocorrectors, antioxidants, warming, analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.).
Methods of pedagogical control
The leading (determining) is the pedagogical control as organically inherent in the process of physical education and constituting an integral part of the pedagogical activity of a specialist.
The term "pedagogical" first of all emphasizes that the control is skillfully carried out by a teacher - a specialist in physical culture and sports - by means and methods acquired by him on the basis of a special physical education and practical work experience in the specialty. Pedagogical control of the process of physical education also uses medical and biological indicators for a comprehensive and in-depth characterization of the state of body systems.
Pedagogical control as a whole traces the relationship and correspondence between pedagogically directed influences, planned results and actually obtained ones. In case of their inconsistency, the necessary decisions should be made and adjustments should be made to the planned process of physical education.
A prerequisite for planning and the initial part of pedagogical control in athletics is the control of the initial level of the athlete's ability to achieve the goals:
-individual level of physical development (in particular, physical qualities);
- fund of motor skills and abilities;
-motivation and individual attitudes to the upcoming activities.
Based on it, the students are divided into groups and the program of the training process is specified.
Control of external factors affecting trainees includes:
- control of external conditions (sanitary and hygienic condition, meteorological information, environmental factors: midlands, increased solar radiation);
- control of the influence of the trainer-teacher (professionalism of actions and observance of the norms of pedagogical ethics).
The control of the motor activity of those involved includes:
-control of the formation and improvement of motor skills and abilities;
- control of the volume and nature of loads, the mode of their alternation with rest;
- control of the interactions of those involved (pair and group mutual influences, as well as interpersonal relationships);
-control of the functional state of the body (functional shift).
It is advisable to assess the general state of the functional capacity of athletes-athletes from the standpoint of the compliance of their main functional systems with the norm.
The state of special physical fitness is best assessed using specific indicators that are adequate to the natural conditions of sports activity and as close as possible to competitive ones.
So the main direction pedagogical control V athletics consists in the analysis of correlations between the dynamics of pedagogically directed influences and pedagogically determined changes in the level of education, development and behavior of students. The inconsistency of real relations with the planned target results determines the need to clarify the direction and parameters of pedagogical influences and make appropriate adjustments to the previously planned plan.
Control data is entered into the accounting documentation of the trainer-teacher in accordance with the official requirements for their maintenance:
1) a journal for recording the work of the group (roster, educational material, class attendance);
2) registration card (accounting for participation in competitions and for athletes);
3) test and competition protocols;
4) medical records (medical control data, maintained by medical workers);
5) logbook of injuries (at sports bases);
6) a book of records of sports achievements;
7) an unofficial document is a working diary of a trainer-teacher. It reflects the practical work experience, content and methodological features of the classes, provides a description of those involved. Diary entries help to comprehensively comprehend pedagogically important facts that are not reflected in official accounting documents.
a log of the presence and condition of equipment, etc.
1.1. Types of pedagogical control
The success of the process of physical education is largely determined by the timeliness of control (its correlation in time with the structural links of this process) and its constancy.
The content of the control is determined by the specifics of the subject and the didactic tasks of the learning stage.
Preliminary control is carried out to determine the possibilities of those involved in mastering physical exercises and fulfilling the standards of the curriculum. It allows you to make clarifications in the planning of educational tasks, means and methods for their solution. You can check the performance of exercises that are structurally similar to the new ones; to test knowledge, skills and abilities after long breaks in classes for planning individual lessons.
Operational control makes it possible to evaluate the decisive moments of pedagogical influences in a lesson (registration of the load of a training exercise, a series of exercises of a holistic lesson) for the operational management of an athlete's activity and achieving the effect of a lesson.
Current control involves continuous control at each training session during the week. The effectiveness of training and the daily change in the state of those involved are determined. The dynamics of the indicators of the individual state between the given and the next lesson is also traced to assess the consequences and the course of the recovery processes (on which the effect of the next lesson depends).
In sports, the parameters of the current load (the sum of operational loads for each lesson) are compared with the results of “estimates” at the end of the microcycle, as well as with indicators current state athlete. The optimal ratio between the zones of load characteristics is determined. A conclusion is made about the quality of training, the change in the athlete's functional indicators for a given period of time (delayed effect). To conduct current control, methods should be used (as in operational control) that require a minimum amount of time without additional effort of trainees. The results of the current control contribute to the refinement of the content of the plan at this stage.
In the textbook L.P. Matveeva (Theory and methods of physical culture, 1991) all 3 types of control are called varieties of operational current control. As a result, his teacher-trainer receives information about motor function involved in athletics, exchanges information with them. This allows the teacher to clarify the means and methods of pedagogical influence on students.
Staged control reveals the main trends in the process of physical education at its relatively long stages.
Methods of biochemical control
When the body adapts to physical stress, overtraining, as well as in pathological conditions, the body's metabolism changes, which leads to the appearance of individual metabolites (metabolic products) in various tissues and biological fluids, which reflect functional changes and can serve as biochemical tests or indicators of their characteristics. Therefore, in sports, along with medical, pedagogical, psychological and physiological control, biochemical control over the functional state of the athlete is used.
In practice, it is usually comprehensive examinations athletes, giving complete information about the functional state of individual systems and the whole organism about its readiness to perform physical activity. Such control at the level of the national teams of the country is carried out by complex scientific groups, which include several specialists: a biochemist, a physiologist, a psychologist, a doctor, and a trainer.
2.1
. Blood tests
For biochemical studies, capillary blood taken from a finger or earlobe is usually used. Venous blood is examined in cases where it is necessary to determine many biochemical parameters and a large amount of blood is required for analysis.
Blood sampling for biochemical analysis is most often performed before and after exercise. Sometimes, to study the dynamics of biochemical changes during the performance of work, as well as to assess the recovery processes, blood sampling can be carried out at different points during the period of work and recovery.
In sports practice, when analyzing blood, the following indicators are determined:
the number of shaped elements;
hemoglobin concentration;
pH indicator;
alkaline blood reserve;
plasma protein concentration;
glucose concentration;
lactate concentration;
concentration of fat and fatty acids;
concentration of ketone bodies;
urea concentration.
It should be emphasized that when interpreting the results of biochemical studies, it is necessary to take into account the nature of the physical work performed.
2.2. Urinalysis
In connection with the possibility of infection when taking blood, urine has recently become the object of biochemical control in sports.
For biochemical studies, daily urine can be used, as well as portions of urine obtained before and after exercise.
In daily urine, the creatinine coefficient is usually determined - the excretion of creatinine in the urine per day per 1 kg of body weight. In men, creatinine excretion ranges from 18-32 mg/day-kg, in women - 10-25 mg/day-kg. The creatinine ratio characterizes the reserves of creatine phosphate in the muscles and correlates with muscle mass. Therefore, the value of the creatinine coefficient makes it possible to assess the possibilities of creatine phosphate resynthesis of ATP and the degree of muscle development. This indicator can also be used to evaluate the dynamics of an increase in creatine phosphate reserves and an increase in muscle mass in individual athletes during the training process.
For biochemical analysis, portions of urine taken before and after exercise are also used. In this case, immediately before performing the test loads, the subjects must completely empty bladder, and urine collection after exercise is carried out 15-30 minutes after its implementation. To assess the course of recovery processes, portions of urine obtained the next morning after the test load can be examined.
2.3. Exhaled air
Exhaled air is collected using a mask with a valve that allows you to direct the exhaled air into a special breathing bag. With the help of devices - gas analyzers in the exhaled air, the content of oxygen and carbon dioxide is determined. Comparing the content of these gases in exhaled and inhaled, i.e. in atmospheric air, the following indicators can be calculated:
maximum oxygen consumption;
oxygen supply;
alactic oxygen debt;
lactate oxygen debt;
respiratory rate.
To determine the MIC and oxygen income, exhaled air is collected during the performance of work, and to calculate the oxygen debt - after the completion of work.
2.4. Saliva tests
Saliva analysis is relatively rare. To obtain saliva, subjects rinse their mouths with a certain amount of water.
Most often in saliva, the pH value and the activity of the amylase enzyme are determined. The activity of this enzyme can be used to judge the intensity of carbohydrate metabolism, since there is a certain correlation between the activity of salivary amylase and the activity of tissue enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism.
2.5. Sweat analyzes
Biochemical study of sweat in athletics is also not often done. To collect sweat, cotton underwear is used, in which the subject performs physical activity, or the subject is wiped with a cotton towel after work is completed. Then the linen or towel is soaked in distilled water, where the sweat components dissolve. The concentrated solution obtained after evaporation in vacuo is subjected to chemical analysis.
The study of sweat allows you to assess the state of mineral metabolism, since sweat is the first to excrete minerals from the body.
2.6. Biopsy of muscle tissue
To obtain a sample of muscle tissue, a microbiopsy is performed: under local anesthesia, a skin incision is made over the muscle under study and a small piece of muscle with a volume of 2-3 mm3 is taken with a special needle. The resulting biopsy is subjected to microscopic and biochemical analysis.
Microscopic examination determines the ratio between the types of muscle fibers, the number of myofibrils and their thickness, the number of mitochondria and their size, the development of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in individual muscle cells.
Biochemical research allows you to determine the concentration of the most important chemical compounds and the activity of enzymes.
Microbiopsy can be performed both at rest and after testing loads.
However, the study of muscle tissue biopsy requires expensive equipment and reagents, as well as the participation of highly qualified specialists. Therefore, such studies are carried out in large laboratories.
Control over the functional state of the body at the training camp can be carried out using special diagnostic express kits for biochemical analysis of urine and blood. They are based on the ability of a certain substance (glucose, protein, vitamin C, ketone bodies, urea, hemoglobin, nitrates, etc.) to react with reagents applied to the indicator strip and change color. Usually, a drop of the test urine is applied to the indicator strip of Glucotest, Pentafan, Medi-test or other diagnostic tests, and after 1 minute its color is compared with the indicator scale attached to the kit.
Instrumental control methods
There are known to be visual and instrumental types of control. The visual one is used much more often, but with the help of the instrumental one can get a digital expression of various characteristics (technique, athlete's condition), more accurate indicators. To control the kinematic characteristics (spatial, temporal, spatio-temporal), photo and video shooting, cyclography are used. Tension platforms (repulsion force) are used to control the dynamic characteristics. To control the economy, a set of sports is used. Instruments. To control the functional state of a bicycle ergometer.
Recovery methods in athletics
Training sessions are the main structural unit of the training process. Their rational planning based on scientific knowledge about the mechanisms of development and compensation of fatigue, as well as the dynamics of the course of recovery when performing various training loads, largely determines the effectiveness of the entire training process. Thus, recovery is an integral part of the training process.
There are several types of restoration of the functional state of the body of athletes. Recovery, which uses pedagogical (alternation of loads, recovery training, recovery days, cycles), psychological, physical (massage, electrical stimulation, water procedures, sauna, baths, recovery by acting on biologically active points), medical methods and means of recovery; vitamins, anabolic drugs (non-hormonal, ointments, rubbing); complex recovery systems.
Massage
There are several types of sports massage:
training;
preliminary (warm-up, tonic or soothing, warming massage);
restorative.
In order for the body to recover faster, it is necessary to use a restorative massage after exercise (both during training and during competitions). That is why it is an important element of sports training. The best effect is achieved when carrying out a restorative massage immediately after hydrotherapy (warm showers, 5-12-minute baths, swimming in the pool) or steam bath, which promote relaxation muscle tissue. When prescribing a restorative massage, first of all, the nature of the performed load (volume, intensity, etc.) is taken into account. At the same time, it should be borne in mind that after prolonged and intense loads, fatigue persists longer than after short-term ones. As a result, the athlete cannot reach the usual level of performance for two or more days.
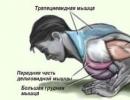
Athletes working at sprint distances spend a large number of energy. In the muscles there is an accelerated breakdown of energy substances under anaerobic conditions, the amount of decay products increases dramatically. When the work ends, the oxygen debt is replenished. Restorative massage is started only after the athlete's pulse and respiratory rate have returned to normal after exercise. As a rule, the time interval between loads and massage is 10-15 minutes. The duration of a massage session depends on the sport, it is 5-10 minutes. With special care, those muscles on which the main load fell are massaged.
At competitions, cases of maximum load are not uncommon. Therefore, stroking should be removed from the set of restorative massage techniques carried out during a break between loads, as it helps to relax the muscles and slows down the motor reaction. It is recommended to apply squeezing, kneading (especially double ordinary, double ring), rubbing with the base of the palm and fingertips. Shaking should be performed after each kneading technique.
When the breaks between loads are 1.5-3 hours, it is useful to do a restorative massage in the shower or after a 3-4-minute stay in a dry-air bath. The duration of the massage should be 7-15 minutes. If conditions do not allow for such a massage, then you need to perform a dry restorative massage. At the end of the massage session, the athlete should get dressed and spend some time in peace. After an hour, “it is advisable to have a second session of a 5-minute private restorative massage. If the first session of restorative massage is carried out immediately after the performance of the athlete, then the recovery period will pass much faster and more evenly, while working capacity will increase.
Middle distance running is heavy duty work. The oxygen-free breakdown of substances in the muscles is very high from the very beginning. As a result, a lack of oxygen occurs in the athlete's body, oxygen debt increases, significant accumulation of under-oxidized decay products in the muscles and large biochemical changes in the blood (adidosis) occur. A restorative massage session, which should be carried out after this kind of physical activity, is scheduled after 10-12 minutes. In this case, the duration of the session is 12 minutes - 6 minutes for each leg: 4 minutes for the thigh, 2 minutes for the lower leg.
The load of submaximal power, as well as the maximum one, can be performed repeatedly. After the first load, a restorative massage is carried out in order to maximize the recovery of the athlete's performance before the start of the re-work. Those muscle groups that carried the maximum load are especially carefully massaged.
4.2. Bath
The bath has been used in sports since time immemorial. It is an integral part of the training process. Many of the effects of the bath procedure (water of different temperatures, dry and humid hot air, broom massage, etc.) contribute to the acquisition and preservation of the best athletic form by athletes.
Hyperthermia primarily affects the skin and muscles. The steam room has a stimulating effect on the muscles, primarily due to the improvement of the blood supply to the muscles, the activation of metabolic processes in it. Hyperthermia gives an increased amount of energy material (glycogen, ATP), accelerates the removal of intermediate and final metabolic products in the muscles - lactic and phosphoric acid. Hyperthermia causes intensification of local metabolism, oxidative processes on the periphery, resynthesis of lactic acid. Muscles are more quickly released from intermediate and final products of energy metabolism, from "fatigue substances", the fatigue phase becomes shorter, physical ability organisms increase. After the steam room, the circumference of the limbs increases by 4-5%, increases muscular strength measured on a dynamometer and a bicycle ergometer. The body is able to withstand prolonged stress due to an increase in reserve alkaline blood. With sweat, chlorine is released, this reduces the acid valences formed as a result of muscle work, increases the ability to bind acidic metabolic products. Taken regularly, the steam bath allows you to actively increase the capabilities of the cardiovascular system so much that it turns out to be equivalent to muscle physical training, and both methods contribute to a gentle training of the heart.
The bath has a beneficial effect on the mobility and dexterity of an athlete, primarily by improving the extensibility and elasticity of the connective tissue structures of his body due to their heating. Added to this is the general relaxing effect of the steam room on the muscles as a result of the shift in the sensitivity threshold of the receptors in the muscles.
The bath is of great importance at all stages of the training process (as an integral part of the training of athletes). The use of the bath after a training session: The bath is used immediately after a workout to relieve fatigue in athletes or reduce its manifestations. At the same time, it is necessary to know that the steam room (and other procedures) represent a certain load, the degree of which depends on the intensity of air heating, its humidity and the degree of cooling, their duration, etc. In addition, the tolerance of the steam room by individual athletes should be taken into account. Under the influence of short-term effects of high temperature in combination with water procedures, positive changes occur in the vegetative sphere, in the activity of the central nervous system. Simultaneously with the improvement of the functional state of the motor analyzer, which is confirmed by an increase in the accuracy and coordination of movements, favorable changes occur in other analyzer systems. In general, the complex of these reactions ensures the fastest recovery of the athlete's performance after performing tiring muscular work and contributes to the appearance of positive emotions, i.e. normalization of psychological perception of large training loads. The following most effective options for using the bath in combination with water procedures are recommended: 1. During the break between morning and evening workouts or competitions in order to quickly restore reduced performance. In this case, it is recommended to stay in the steam room no more than 2 times for 3-4 minutes at a temperature of 80-100 ° C, air humidity in the steam room up to 30%. After each visit to the steam room, it is necessary to take a cool shower (or pool) with a water temperature of 15-18 ° C for 15-20 seconds, then a shower or bath with a water temperature of 35-40 ° for 1-1.5 minutes. After that, the athlete should rest calmly (preferably lying down) for 5-7 minutes. 2. During breaks between trainings or competitions lasting more than 18-20 hours or performing a large amount of work followed by a day of rest, it is recommended to use the bath for 3 or 5 times in a steam room for 5-7 minutes at a temperature of 90-100 ° , air humidity up to 30%. Total time for the whole complex of procedures should not exceed 1.5-2 hours. If they use a broom, then the humidity can be increased by spraying water on the walls or pouring water on the stove stones. After each entry, water procedures are taken, but the duration of a cold shower or bath in this case should not be more than 3-4 s. The duration of a warm shower or bath, on the contrary, increases to 2.5-3 minutes. The rest time between visits to the steam room also increases, it can be increased at will and the well-being of the athlete. The number of visits to the steam room can be increased up to 5-7 times, but the time spent in the steam room should not be increased. The temperature of the water in the pool or bath is within 26-30°C. In all options for using the bath, it is recommended to take soft drinks, juices, mineral water. The frequency of using the above complexes depends on the nature of the training loads and the complex of thermo-hydroprocedures: in the first option - 3-7 times a week, and in the second - no more than 2 times a week.
Conclusion
From all the above material, it is easy to conclude that in the process of training it is necessary to pay great attention to the control over the functional state of the athlete, as well as to provide timely and correct assistance to the recovery processes that take place in the athlete's body throughout the entire training process. In the modern world, there are a sufficient number of methods and means of control and recovery. Unfortunately, the material base of sports schools and colleges does not allow covering all the means. Therefore, it is necessary to focus on the use of more accessible methods and means. These are pedagogical methods of control, pedagogical and physical means of recovery. With the right organization integrated approach to the training process, the growth of sports results that do not harm the health of the athlete is guaranteed.
Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine
Donetsk National University of Economics and Trade
named after Mikhail Tugan-Baranovsky
Department of Physical Education
"Medical control and self-control of athletes"
Completed:
Lukyanenko D.I., OA-09-Sb
Checked:
Starichkov G.A.
Donetsk, 2010
Introduction………………………………………………………………………...........3
1. Medical control of athletes…………………………………………….4-5
2. Functional tests, tests…………………………………………………6-14
3. Self-control in the process of physical education and sports …………… 15-18
Conclusion ……………………………………………………………………........19
List of used literature ………………………………………..........20
Introduction
A person as a person is formed in the process of social life: in study, work, in communication with people. Physical culture and sports contribute to the formation of a comprehensively developed personality.
Moral education. During classes, trainings, and especially during sports competitions, students endure great physical and moral stress: a rapidly changing environment, the opponent's resistance, the dependence of the result of sports competitions on the efforts of each team member, the ability to subordinate their interests to the interests of the team, respectful attitude towards the opponent contribute to the formation of such character traits as willpower, courage, self-control, determination, self-confidence, endurance, discipline.
Mental education. At physical culture and sports lessons, students acquire knowledge about rational ways of performing motor actions, about using the acquired skills in life, learn the rules of hardening the body, mandatory hygiene requirements.
Observation, attention, perception develop, the level of stability of mental performance increases.
Studies show that physical exercises contribute to the improvement of the sense organs, muscle-motor sensitivity, visual and auditory perception, the development of memory, especially visual-motor.
Labor education. The essence of labor education lies in the systematic and planned development of the qualities and properties of the individual, which determine the preparation of a person for life, for socially useful work. Diligence is also brought up directly in the process of doing physical exercises and sports, when those involved in order to achieve maximum results, overcoming fatigue, repeatedly perform physical exercises.
Aesthetic education. In physical culture and sports there are huge opportunities for the aesthetic education of a person, the development of the ability to perceive, feel and correctly understand the beautiful in actions, in the beauty of the perfect forms of the human body, in the movements of a gymnast, acrobat, brought to the degree of art, diver, figure skater. Performing exercises to music in rhythmic gymnastics, figure skating contributes to the development of musical culture. Hiking, climbing, sailing and other sports allow you to understand and feel the beauty in nature.
The connection of physical exercises with aesthetic education has a dual character, since it allows not only to form an outwardly beautiful image, but also to influence the education of moral and volitional qualities, ethical standards and behavior in society at the same time.
1. Medical control of athletes
Medical control is a system of medical research conducted jointly by a doctor and a coach (teacher) to determine the impact of training loads on the body of a student.
Medical examinations of persons involved in physical culture and sports are divided into primary, repeated and additional.
During the primary medical examination, the doctor decides on admission to physical education and sports. Without the permission of a doctor, a coach or teacher of physical education has no right to allow a beginner to practice. During a medical examination, the state of health, physical development and adaptability of the body to dosed physical activity are determined. Such a survey is of great importance in mass physical culture, as well. the presence of a number of diseases is an absolute or relative contraindication to exercise.
During repeated medical examinations, the influence is determined regular classes physical culture and sports on the state of health. Physical development and functional state of the athlete's body. Such examinations are mandatory for all athletes at least once a year.
Additional medical examinations are organized to resolve the issue of admitting athletes to competitions, as well as to resolve the issue of the possibility of starting training after illnesses or injuries, after long breaks in classes, in case of overwork (on the recommendation of coaches or at the request of athletes).
The doctrine of physical development. Medical control over those involved in physical culture and sports provides, as mentioned above, the study of physical development.
Physical development is understood as a complex of functional and morphological properties of the organism, which determines the physical capacity of the organism. Thus, the concept of "physical development" includes not only the morphological features of the structure and size of the body, but also the functional capabilities of the body.
Physical development is determined by endogenous (internal), exogenous (external), and socio-economic factors. The study of individual physical development is carried out by calculating various morphological indicators, such as height, body weight, chest circumference, specific body weight, its fat, muscle and bone mass, etc. in the study of adults, these morphological features serve as a criterion for the physical conditions of the organism, and for children, in addition, as criteria for the correctness of their growth and development.
Indicators of the physical development of an adult do not remain unchanged. Especially clearly they change with aging. Therefore, it is necessary to take into account the correspondence of physical development to the stage of biological development.
The criteria for physical development are also features of the physique. Under the physique understand the dimensions, shapes, proportions (the ratio of some body sizes to others) and features of the relative position of body parts.
Features of the physical development and physique of a person are largely determined by his constitution. The constitution of a person, manifested, in particular, in the features of the physique, depends both on hereditary factors, past illnesses, working conditions, physical exercises and sports. Of the external factors under the influence of which the constitution changes, physical exercises and systematic sports are of particular importance, especially in childhood.
The main methods for studying physical development are external examination (somatoscopy) and anthropometry. Along with them, the following are used: the photographic method, radiography, measuring the shapes of the human body with the help of special devices, measuring the angles on the body with the help of goniometers.
Somatoscopy. An external examination begins with an assessment of posture. Posture is the habitual posture of a person, the manner of standing and sitting. Posture is usually assessed in a standing position. Posture is examined from head to toe. The position of the head is evaluated in relation to the position of the body. Then proceed to the description shoulder girdle. Great importance is given to the description of the spine. The severity of the physiological curves of the spine is determined, the shape of the back is determined. They also evaluate the shape of the legs, the shape of the foot. The degree of muscle development is assessed as good, satisfactory, weak. The uniformity of its development and relief are determined, i.e. how pronounced the muscle pattern is.
With somatoscopy, body type and body proportions are determined.
Anthropometry. Anthropometric measurements supplement and refine the data of external examination, make it possible to more accurately determine the level of physical development of the subject. Repeated anthropometric measurements make it possible to monitor the dynamics of the physical development of children and take into account its changes during systematic physical exercises and sports.
In anthropometric studies of athletes, the following indicators are usually determined: standing and sitting height, body weight; diameters - shoulder width, anteroposterior and transverse diameters chest, the width of the pelvis; circumference - neck, chest, shoulder. thighs and shins; length of limbs and individual segments. The main indicators of physical development are height, weight and chest circumference.
2. Functional trials, tests
Comprehensive analysis of medical examination data, results of application of instrumental research methods and materials obtained during functional tests, allow an objective assessment of the readiness of an athlete's body for competitive activity.
With the help of functional tests, which are performed both in the laboratory (in the functional diagnostics room), and directly during training in gyms and in stadiums, the general and specific adaptive capabilities of the athlete's body are checked. According to the test results, it is possible to determine the functional state of the organism as a whole, its adaptive capabilities at the moment.
Testing allows you to identify the functional reserves of the body, its overall physical performance. All medical testing materials are not considered in isolation, but in a complex with all other medical criteria. Only a comprehensive assessment of the medical fitness criteria allows one to reliably judge the effectiveness of the training process for a given athlete.
Functional tests began to be applied in sports medicine at the beginning of the twentieth century. Gradually, the arsenal of samples expanded due to new tests. The main tasks of functional diagnostics in sports medicine are the study of the body's adaptation to certain influences and the study of recovery processes after the cessation of exposure. It follows from this that testing is in general identical to research. "black box" used in cybernetics to study functional properties regulation systems. This term conditionally denotes any object whose functional properties are unknown or insufficiently known. The "black box" has a number of inputs and a number of outputs. To study the functional properties of such a “black box”, an impact is applied to its input, the nature of which is known. Under the influence of the input action, response signals appear at the output of the "black box". Comparison of input signals with output signals makes it possible to evaluate the functional state of the system under study, conventionally designated as a “black box”. With perfect adaptation, the nature of the input and output signals is identical. However, in reality, and especially in the study of biological systems, the signals transmitted through the "black box" are distorted. By the degree of signal distortion during its passage through the "black box", one can judge the functional state of the system or complex of systems under study. The greater these distortions, the worse the functional state of the system, and vice versa. Abstract >> Physical culture and sports
The nature of the reaction of the athlete's body by medical control And self-control, with the help of the coach's observations and readings... an exact science. - M., 1979. Bondarchuk A.P. Training athlete. - Kyiv, 1986. Verkhoshansh Yu.V. Programming and organizing...
Physical culture in the general cultural and professional training of students
Abstract >> Culture and artConcepts 99 7.2. Medical control 100 7. 3. Pedagogical control 101 7.4. self control 102 7.4.1. Subjective indicators self-control 103 7.4.2. Objective ... athletes, among whom there were 47 athletes, performed on V Olympic Games ah in Stockholm...
The use of illegal drugs and doping methods in modern sports.
Abstract >> Medicine, healthRequires careful laboratory and medical control, as it is fraught with possible ... can lower pressure, weaken self-control and evoke feelings of euphoria. When ... problems were, perhaps, only athletes. In samples of Americans Jude Logan and...
Cheat Sheet on Physical Education
Cheat sheet >> Culture and artImproving well-being and mood, self-control and self-esteem, increasing feelings of ... equipment 5) violation of the rules medical control 6) unfavorable sanitary and hygienic... sports swimming equally, athlete- triathlon, pentathlon and...
Development control physical qualities
Development control strength carried out using the following groups of methods.
The first group is based on the determination of the maximum static strength of the main muscle groups using a dynamometer. This technique is called polydynamometry. The measurement data make it possible to characterize the power "topography" of the athletes' muscles, identify strong and weak muscle groups.
The second group of methods is to measure the dynamic strength of the muscles. Here, with the help of jumping exercises, you can determine the ability to repeatedly manifest dynamic strength. The length or height of the jump is measured in linear units or the time taken to complete the jumps.
Development control you were fast. Control should include testing of all four forms of quickness:
1. To determine the speed of a motor reaction, the latent (hidden) reaction time (in milliseconds) is measured. 2. Maximum frequency of movements during exercise chosen kind athletics. For example, sprint time is determined by counting the number of steps per unit of time over a certain distance. 3. The speed of individual movements in the general cycle of running, jumping and throwing is determined by analyzing cinematographic records, recording efforts, time of support and flight phases (podometry method) using strain gauge and dynamometer equipment. 4. A complex manifestation of speed is evaluated by pedagogical tests. Distance running is measured (registered maximum speed running), jumping and throwing (the execution time and the number of movements per unit of time are recorded).
Development control endurance. Control is carried out with the help of biomedical and pedagogical tests. A wide variety of control methods is due to the fact that endurance is multifactorial. Biomedical tests evaluate the level of development of various body functions, their limit values and economy. Pedagogical testing is necessary for a comprehensive assessment of endurance. All exercises are performed in competition conditions.
Development control dexterity. When assessing dexterity, various criteria are used, but none of which is yet generally accepted. In the practice of determining the quality of dexterity, to some extent, they are judged by the time spent on mastering new norms of motor actions or the accuracy of movements used to assess the degree of perfection of sports equipment or time spent in the test.
Development control flexibility. The measure of flexibility is the maximum range of motion in the joints. Flexibility is measured in degrees or in linear units. A goniometer is used to measure the degree of mobility in degrees. The measurement of flexibility in linear measures is based on determining the path of the distal part of the body link moved in space from the initial position (or a certain plane) to the highest point of the movement amplitude. The distance over which a certain point of the moving link of the body moves is measured.
ATHLETICS- one of the main and most popular sports, combining various exercises in running, race walking, jumping and throwing. In the sports classification, there are St. 60 varieties of athletics exercises. The program of the Olympic Games includes 24 types of track and field exercises for men and 16 for women.
Run- the main exercise in L. a., which has the most versatile effect on the body, since almost all the muscles of the body are involved in the work and the activity of the fiziol is activated. systems. The intensity and duration of the impact of running exercises on the body is determined by the length of the distance. The shorter it is, the more intense the work. Running on short distances(from 60 to 400 w) and hurdling is performed at maximum intensity, this is a typical speed exercise. Middle distance running (800-1500 m) is a work of submaximal intensity. Running for long (3-10 thousand m) and ultra-long distances (up to 42 km 195 m) and hurdles are performed with high and moderate intensity and, by the nature of the effect on the body, is an endurance exercise. The longer the running distance, the more physiological, changes in the body (increased heart rate and respiration, increased systolic and minute blood volume, increased blood pressure, etc.) are more pronounced and the recovery period is longer (see Running).
Race walking- exercise, in which movements are worn cyclical; differs from running in the absence of the so-called. flight phases, and from normal walking - more energetic movements with greater amplitude. The main distances in the competitions for men are 20 and 50 km, for boys - 3-10 km. Walking exercises develop endurance. During strenuous training and competition, large functional changes in the body are noted: oxygen consumption reaches 1.5-2.5 l / min, pulmonary ventilation - 15-25 l / min, heart rate - 180-200 beats per 1 min., systolic blood pressure - up to 180-200 mm Hg. Art. and more, weight loss - up to 3-4 kg. The recovery period after training and competition - sometimes up to 1 - 2 days. and more; its duration depends on the degree of fitness of the athlete.
jumping(in length, height, triple and with a pole) - exercises of a speed-strength nature with acyclic movements, combining elements of sprinting (running) and including a complex coordination act associated with repulsion, flight and landing. Make great demands on the nervous and muscular systems e, vestibular, visual, tactile analyzers. Shifts in blood circulation and respiration are relatively small due to the short duration of the load: the heart rate usually does not exceed 140-160 beats per 1 minute, systolic blood pressure - 150-160 mm Hg. Art., systolic blood volume 80-100 ml, weight loss - 0.2-0.5 kg. The recovery period is within 20-30 minutes, but since the exercises are repeated many times in training and competitions, the shifts can reach much larger values and the recovery period sometimes drags on up to several hours.
Throwing- exercises in throwing various projectiles at a distance. They are divided into several types: discus, hammer, spear, grenade, ball, shot put, etc. high level development of muscle strength, speed and coordination of movements. The greatest fiziol, shifts at throwings are observed from a muscular, nervous system and a vestibular analyzer. Changes in the functions of blood circulation and respiration are relatively small. But since the competition (as in jumping) lasts a long time (up to several hours), in general, the energy consumption is high and the recovery period can be extended up to 2-3 hours.
all-around- complex view of L. a. - combination various kinds running, jumping and throwing. classic views all-around for adults - decathlon for men (100, 400, 1500 m and 110 m hurdles, long jump, high jump and pole vault, javelin and discus throw, shot put) and pentathlon for women (200 m and 80 m run). m hurdles, long jump and high jump, shot put). All-around classes make the greatest demands on the body and contribute to a versatile physical. development, since the conditions of training and competition require a change in various physical. exercises. Fiziol, shifts after each exercise are due to its nature, the total energy consumption and shifts in the activity of various systems reach significant values. Competitions are held for two days. The recovery period is delayed up to 24 hours. and more.
The effect of athletics on the body
Regular, systematic classes L. a. promote harmonious physical. development, health promotion, the formation of a variety of vital motor skills, the development of speed, strength, dexterity, endurance, the expansion of funkts, capabilities of the body, increasing its resistance and resistance to adverse meteorol, influences. The degree of impact of certain types of athletics exercises on the body is determined by their nature, intensity and duration. Increases in track and field athletes muscle mass, the ability to maximize tension and relaxation, increases muscle strength(especially in sprinters, throwers and jumpers), coordination of movements improves, speed and accuracy of motor reactions increase. Most fast response sprinters, jumpers and throwers differ. The function of the analyzers (especially visual and vestibular) is improved to the greatest extent in jumpers and throwers. Athletes who train regularly improve their functions respiratory system, the vital capacity of the lungs increases (up to 5-6 thousand ml or more) and the maximum pulmonary ventilation (up to 150-200 l / min), as well as the diffusion capacity of the lungs and tissue respiration. Increased resistance to hypoxia. The functions and possibilities of the cardiovascular system are significantly expanded. The volume of the heart increases to 800-1000 cm3 or more, moderate myocardial hypertrophy develops, the work of the cardiovascular system becomes more economical: the pulse slows down to 40-64 beats per 1 minute, systolic blood pressure decreases to 100-115 mm Hg. Art., systolic volume increases, blood flow slows down somewhat, diastole lengthens, myocardial contractility increases, peripheral blood resistance decreases. Increase funkts, opportunities of respiratory and cardiovascular system in the course of regular occupations L. and. the greater, the higher the proportion of exercises in it that contribute to the development of endurance, i.e., when doing running, walking, all-around. Changes in the nervous, muscular systems and analyzers are most pronounced in athletes involved in hurdling, throwing and all-around.
Athletes have, as a rule, a proportional physique. Athletes who specialize in different types L. a., have some characteristic morphofunctional features that contribute to the achievement of high sports results. Thus, long-distance runners are more likely to be of average height with relatively heavy weight body, large respiratory volume of the lungs. Athletes specializing in hurdling and jumpers, as a rule, are tall, relatively light in body weight, long legs with well-developed muscles; throwers - high growth, large body weight, broad shoulders, powerful muscles, large physical. by force.
Medical control
In the course of selection of sportsmen for employment L. and. and in the process of training, qualified medical supervision is very important. Its mission is to help maximize health effect occupations, the prevention of diseases and injuries, etc. Contraindications for occupations L. and. coincide with general contraindications for sports (see Medical control). Sports training in sprinting, in long and high jumps can be started in children from 10-12 years old, in hurdling and throwing - from 13-14 years old, in pole vaulting - from 15-16 years old. Athletes are allowed to compete after 1 - 1.5 years systematic studies. Competitions and trainings are held according to the following age groups: teenage (11 - 12 years old), junior youthful (13-16 years old), senior youthful (16 - 17 years old), youthful (18-19 years old), youth (20 years old - 21 years old). The length of the distance, the weight of the projectiles, the height of the barriers are determined taking into account the age and gender characteristics of the athletes. So, for children and women, competitions in running for long and extra long distances and in race walking, in hammer throwing, pole vaulting, triple jump (for women), and decathlon are excluded.
Of the most common injuries in athletes, it should be noted myositis and damage to the muscle fibers of the two -, quadriceps femoris muscles, ankle sprains in sprinters and jumpers (in the latter, in addition, bruises in the heel area and damage to the calcaneus); inflammation and damage to the calcaneal (Achilles) tendon, periostitis of the tibia, damage to the bursal-ligamentous formations of the ankle joints in middle and long-distance runners; damage to the bag-ligament formations of the shoulder, elbow joints and brushes, as well as the muscles of the shoulder girdle in throwers. With irrational training and physical. overvoltage, dystrophic changes in the myocardium can be observed (mainly in athletes involved in the types of L. a., developing endurance), osteochondrosis of the spine and radiculitis (ch. arr. in throwers).
Bibliography: Medical observations of athletes during training, ed. Edited by N. D. Graevskaya and S. P. Letunov. Moscow, 1966. GraevskayaN. D. The influence of sports on the cardiovascular system, M., 1 975, bibliogr.; Athletics, ed. Edited by N. G. Ozolina and D. P. Markov. Moscow, 1972. Fundamentals of athletics, comp. A. F. Boyko, M., 1976; Human Physiology, ed. N. V. Zimkina, Moscow, 1975.
N. D. Graevskaya, N. G. Ozolin.